THE ECSEL CURRICULUM LIBRARY (ECL)
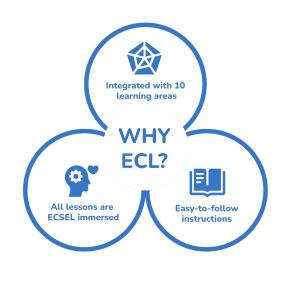
Why ECL?
The ECSEL Curriculum Library (ECL) is a destination for teachers to find ECSEL-integrated curriculum activities that have been designed with an emergent mindset. Each activity incorporates ECSEL language, tools, and/or techniques and includes easy-to-follow material lists, instructions, ECSEL prompts to support children in learning about emotions, ways to extend children’s thinking, and desired learning goals that are linked to our ECSEL Standards. ECL has a large variety of topics and learning areas, and makes teaching (and learning) easy and fun!
How the ECSEL Curriculum Library Works
CHOOSE A PLAN
Find a membership plan that best fits your needs and become a member of ECL.
GET ECL CREDITS
After you become an ECL member, you will receive monthly ECL credits based on the plan your chosen plan.
BUY LESSONS
Use your ECL credits to purchase the lessons you need!
Lesson Title
Find out what development level this lesson is for and what learning areas are included.
Overview
Read a short description of the lesson.
ECSEL Standards & Learning Goals
Gain a clear idea of what the goals of this lesson and what ECSEL standards it aligned with.
Materials & Instructions
Here is gist of the lesson, including the materials you will need and a step-by-step guide to teach.
ECSEL Prompts
Read the questions you can ask to promote ECSEL thinking and discussions!
Extended Learning
Need more ideas to extend children’s learning? We have you covered!

What is ECL?
The ECSEL Curriculum Library (ECL) is a curated and growing collection of ECSEL-integrated and CASEL-aligned digital activities and lesson plans for children from infancy through pre-kindergarten. All lessons have a social-emotional learning component no matter if you are doing art, science, math, engineering, or more!
What is ECSEL?
ECSEL is Housman Institute’s emotional, cognitive, and social early learning philosophy. It is based on over 35 years of research, and is the foundation of our unique, evidence-based flagship training program, begin to ECSEL.
Through begin to ECSEL, educators learn how to begin teaching emotional competence starting from birth, gain a better understanding of their role as key socializers in children’s lives, and are given extensive support in understanding and learning to manage their own emotions and stress. Begin to ECSEL is designed to be woven seamlessly into any existing curriculum or program, which is why we developed the ECSEL Curriculum Library — to help educators jumpstart this integration, and begin having important conversations with children about emotions during any part of their day.

E motional
C ognitive
S ocial
E arly
L earning
The ECSEL Standards
The ECSEL Standards were developed with Housman Institute’s philosophy in mind – going beyond SEL to both nurture and support children’s cognitive capabilities, as well as their social and emotional skills, from birth. Cognitive skills including executive function, working memory, self-regulation, asking questions, and problem-solving are all important components in the overall ECSEL philosophy, and play a crucial role in helping to strengthen children’s emotional intelligence.
EMOTIONAL IDENTIFICATION
Definition: Children’s ability to recognize and identify different emotions. As children develop their emotion knowledge, they will begin to recognize and identify facial expressions that represent different emotions in themselves and in others. Emotional identification is one of the two quadrants of emotional intelligence that makes up emotion knowledge.
EMOTIONAL UNDERSTANDING
Definition: Children’s ability to understand their emotions and the emotions of others. As children develop their emotion knowledge, they will begin to understand the differences between and among emotions, be aware of emotions, and be able to discern emotions accurately. Emotional understanding is the second of the two quadrants of emotional intelligence that makes up emotion knowledge.
EMOTIONAL EXPRESSION
Definition: Children’s ability to express their emotions accurately and constructively. Emotional expression is one of the two quadrants of emotional intelligence that make up emotion regulation.
EMOTIONAL REGULATION
Definition: Children’s ability to manage and cope effectively with heightened emotions, both positive and negative. Emotional regulation means managing our behaviors, feelings, and thoughts. Without emotional regulation, it is difficult to learn. Emotional regulation is the second of the two quadrants of emotional intelligence that make up emotion regulation.
CAUSE & EFFECT
Definition: Children’s ability to understand the causes of their emotions and how their emotions impact their behaviors. When children are able to understand the reasons behind their emotions and the effect they can have on their behaviors, they can develop key social-emotional skills such as self-awareness, perspective taking, relating to others, and the ability to be empathetic and understanding of others.
EMPATHY AND PROSOCIAL SKILLS
Definition: Empathy can be defined as the ability to understand how another person might be feeling and respond sensitively. Prosocial behaviors are the acts of helping, comforting, sharing, and cooperating with others for their benefit. Inclusivity means understanding others from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and contexts to provide learning experiences that allow students to thrive. These are all critical in supporting the positive development of children’s identity and sense of self.PROBLEM SOLVING
Definition: Children’s ability to recognize and identify a problem or conflict and use environmental cues and the building blocks of emotional intelligence to ask for help or manage the problem/conflict with or without support. For infants and toddlers, this can look a lot like imitation of behaviors (teacher/caregiver and peer), taking initiative (grabbing a toy, arguing), and emotional identification. For preschool age children and older, this relates more to their ability to recognize social and ethical problems, or recognizing when they need help.The ECSEL Standards align with CASEL, Head Start, NAEYC, and Massachusetts SEL standards, while also going above and beyond by including social, emotional, and cognitive skill development that can be supported by educators within each standard.
Developmental milestones for children from infancy through pre-kindergarten are also included within each of our seven standards so educators can meet any child where they are and support their social, emotional, and cognitive early learning from birth.
